In today’s digital age, hacking has become an increasingly feared phenomenon. Some hackers view their activities as a form of activism, a means to wealth, or a way to exact revenge. However, many people are unaware of the legal consequences of hacking, even if it involves someone they know personally.
Understanding Hacking
The term “hacking” is often misinterpreted as solely involving the use of specialized programs or equipment by tech-savvy individuals. In reality, hacking simply refers to gaining unauthorized access to information stored on a computer.
Accessing someone’s emails, messages, or accounts without their consent constitutes hacking, regardless of the individual’s relationship to the victim. This can include friends, family members, or romantic partners and is recognized as a criminal act in many jurisdictions.
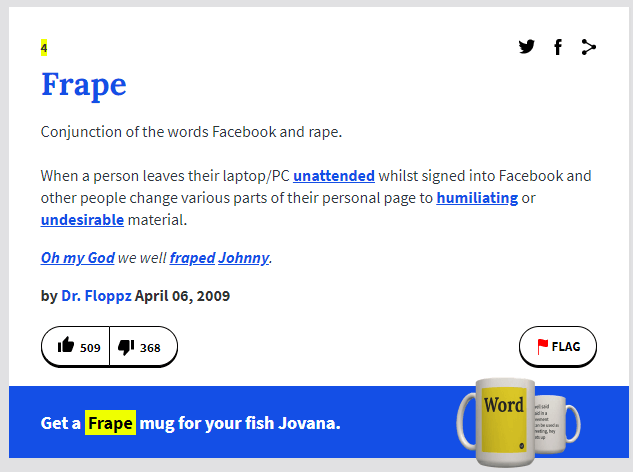
Even actions such as ‘fraping’ are considered hacking and may result in severe legal consequences if the victim chooses to press charges.
No Hacking is Innocent

Many individuals do not view accessing a partner or friend’s email or social media account as a criminal act. However, in most countries, doing so without permission is illegal.
In one notable case, a man in the US faced a potential 5-year prison sentence for reading his wife’s emails. He only avoided incarceration because his wife had committed the same offense.
Although some individuals on the UK forum Mumsnet believe that accessing an unfaithful spouse’s emails is legal, UK legal experts disagree.
Regardless of the method used to gain access, reading a partner’s emails or messages without their consent is considered a crime in most jurisdictions.
Serious Consequences of Social Media Hacking
Social media platforms are often prime targets for hackers. A survey from 2009 revealed that a third of teenagers had experienced social media hacking. Despite its widespread occurrence, social media hacking is an offense punishable by law, and those convicted may face severe prison sentences.
In 2012, a UK court sentenced a man to 12 months in prison for hacking into a stranger’s Facebook account. US attorneys regularly handle lawsuits resulting from hacked social media accounts.
Even seemingly innocent actions, such as posting content on a friend’s page as a joke, can lead to serious legal ramifications. In one instance in 2010, a student was fined £10,000 for accessing a friend’s Facebook account and altering their status.
If you’re concerned about social media security, consider ordering a comprehensive security audit here.
Long-term Consequences of Hacking
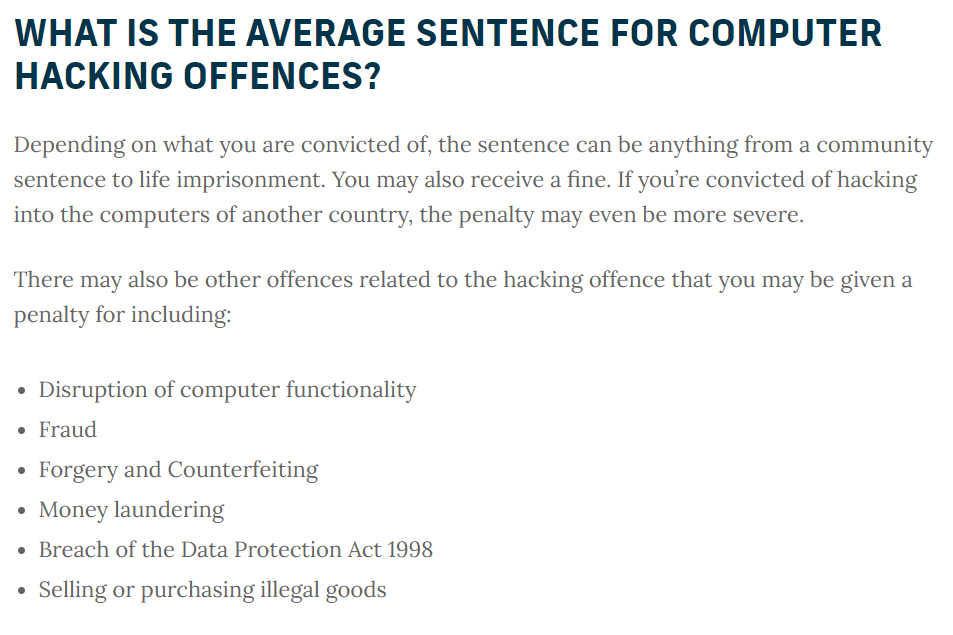
The severity of the legal consequences for hacking depends on the nature of the offense and the jurisdiction in which it occurs. Sentences can range from fines to life imprisonment. Unlawfully accessing someone’s account is a serious invasion of privacy and can have long-lasting effects on the victim’s life.
The psychological impact of hacking on victims can be significant, with some individuals experiencing depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
In the UK, the Computer Misuse Act of 1990 governs hacking activities. This comprehensive legislation addresses various aspects of hacking, from unauthorized access to data modification. As such, even seemingly innocuous actions like changing a friend’s social media status or logging into their account without permission are considered criminal offenses.
In the United States, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) is the primary legislation concerning hacking. Initially designed to protect corporate data from espionage, the CFAA has undergone several amendments since its introduction in the 1980s and now covers most computers across the country.
If you’ve been a victim of hacking, seek immediate assistance from our team here.
Real-World Examples of Hacking
There have been numerous high-profile hacking incidents in recent years. Some notable examples include:
Equifax Data Breach: In 2017, the credit reporting agency Equifax experienced a massive data breach that exposed the personal information of approximately 147 million individuals. The breach resulted in settlement of $575 million.
Sony Pictures Hack: In 2014, Sony Pictures suffered a significant cyber attack that led to releasing of sensitive information, including employee data and unreleased films. The US government attributed the attack to North Korea, which was seen as retaliation for the film “The Interview.”
Yahoo Data Breach: In 2013 and 2014, Yahoo experienced two separate data breaches that compromised the accounts of 1 billion and 500 million users, respectively. The breaches were not disclosed until 2016, and Yahoo later agreed to pay $50 million in damages to the affected users.
WannaCry Ransomware Attack: In 2017, the WannaCry ransomware attack affected over 200,000 computers across 150 countries. The attack targeted Windows operating systems and encrypted user data, demanding a ransom for its release. The attack significantly impacted the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) and other organizations worldwide.
Target Data Breach: In 2013, US retailer Target suffered a data breach that exposed the credit card information of approximately 40 million customers. The breach led to the company settling for $18.5 million with 47 US states and the District of Columbia.
These real-world examples highlight the importance of understanding the potential legal consequences of hacking and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data.
Preventing Hacking and Ensuring Cybersecurity
Given the severity of the legal consequences of hacking and the potential damage to individuals and organizations, it’s crucial to take proactive measures to ensure cybersecurity. Here are some essential steps to protect yourself and your digital assets:
Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Create complex passwords that include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using the same password across multiple accounts, and consider using a password manager to keep track of your passwords securely.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Activate 2FA for all your online accounts, including email and social media. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a secondary authentication method, such as a fingerprint or a one-time code sent to your mobile device.
Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update your operating systems, applications, and antivirus software to protect your devices against known security vulnerabilities.
Be Cautious with Email: Be wary of phishing emails that trick you into revealing sensitive information or installing malicious software. Verify the sender’s identity, and never click on suspicious links or download attachments from unknown sources.
Secure Your Wi-Fi Network: Protect your home or office Wi-Fi network with a strong password and encryption. Disable remote administration and change the default login credentials for your router.
Back-Up Your Data: Regularly back up your data to an external hard drive or a secure cloud storage service. In case of a ransomware attack or data breach, having a backup will help minimize the damage and facilitate recovery.
Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices. Educate your family, friends, and colleagues about the importance of online security and the potential legal ramifications of hacking.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to hacking and ensure the security of your digital assets. In case of a security breach, seek immediate assistance from our team here.
Remember that hacking is a serious offense with severe legal consequences. Protect yourself and your organization by implementing robust cybersecurity measures and fostering a culture of online security awareness.
Featured image by Roman Chazov from Shutterstock.com